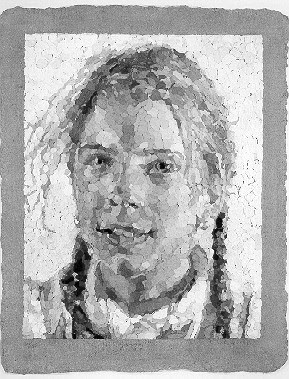Chuck Close: A Systematic Approach to Portraiture
In this collage portrait of Phillip Glass, titled Phillip, by Chuck Close, one can see an overall structure of tonal values, whereby the artist successfully employs a full range in scale of white-to-black. Notice how values are placed according to similarity and proximity, and it is this carefully selected combination that makes it possible to render the portrait. Also, see how significant the grid system is in this piece, with incremental units evenly divided.
In order to create such a rendered composition, one must acutely observe the subtle shifts in light and shadow, form and volume. It is an organized, laborious, and systematic approach to constructing an image, and relies on the artist's ability to maintain extreme focus at every stage of the execution.
This can be seen in another Chuck Close example of a portrait, titled Georgia, which is constructed of handmade paper. Evident, as with so many incredible examples of his work, is his highly methodological, formal analysis of information.
"The remarkable career of artist Chuck Close extends beyond his completed works of art. More than just a painter, photographer, and printmaker, Close is a builder who, in his words, builds "painting experiences for the viewer." Highly renowned as a painter, Close is also a master printmaker, who has, over the course of more than 30 years, pushed the boundaries of traditional printmaking in remarkable ways.
Almost all of Close’s work is based on the use of a grid as an underlying basis for the representation of an image. This simple but surprisingly versatile structure provides the means for "a creative process that could be interrupted repeatedly without…damaging the final product, in which the segmented structure was never intended to be disguised." It is important to note that none of Close's images are created digitally or photo-mechanically. While it is tempting to read his gridded details as digital integers, all his work is made the old-fashioned way—by hand.
Close’s paintings are labor intensive and time consuming, and his prints are more so. While a painting can occupy Close for many months, it is not unusual for one print to take upward of two years to complete. Close has complete respect for, and trust in, the technical processes—and the collaboration with master printers—essential to the creation of his prints. The creative process is as important to Close as the finished product. "Process and collaboration" are two words that are essential to any conversation about Close’s prints." – via Chuck Close: Process and Collaboration
Links:
Chuck Close Exhibit at the Walker
Chuck Close Exhibit at the MOMA
Chuck Close Portfolio at Pace Prints
Self Portraits: Young Artists Create Oil Pastel Mosaics
Young Students Collaborate to Make a Portrait
 artist,
artist,  design process,
design process,  great thinkers,
great thinkers,  painting,
painting,  photography,
photography,  portrait,
portrait,  printmaking
printmaking